| Version 1 (modified by , 17 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
Table of Contents
Building our own Testbed
In this section we give a detailed description of our efforts on setting up a mid-size ORBIT-like testbed. In the right of this page you can see a list of all the related actions we had to take from the initial stage until the stage of having a full functional testbed that can be remotely accessed for uploading particular experiments, running the experiments and collecting the results.
Hardware Setup
Orbit Node
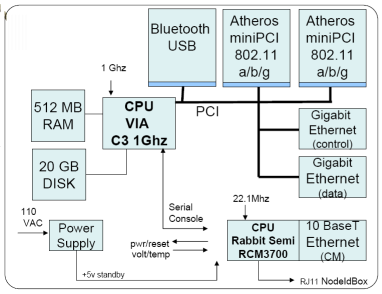
Each ORBIT Radio Node is a PC with a 1 GHz VIA C3 processor, 512 MB of RAM, 40 GB of local disk, two Ethernet ports, two 802.11 a/b/g cards and a Chassis Manager to control the node, see Figure 3. The description about the ethernet ports is following.
Control port - The ethernet port between 4 USB ports, it is a Rtl-8169 Gigabit ethernet port, which is used to load and control the ORBIT node and collect measurements.
Data port - The ethernet port above two USB ports, it is a VT6102 Rhine-II 100/10baseT Ethernet port, which is used for data communication,
CM port - The 10BaseT Ethernet port on Chassis Manager Card, which is used to communicate with gridservice (not gridservice2)
Testbed
The test bed consists of nodes and several servers. Technically, all servers can be put in one machine with at lease two ethernet ports, but it's not recommendatory because of potential security consideration. A typical test bed include three servers discribed below
Services - It is used to host various services including DHCP, DNS, NTP, TFTP, PXE, Frisbee, NFS, mysql, OML and Apache. We have different aliases for the management host to segregate the services that it hosts. This machine or port shall be connected with Control port of nodes.
Console - It is used to run experiments with nodehandler4. Console is also connected with Control port of nodes. It may share one Ethernet port with Services. A better way is setuping a console in one machine exclusively and let it accessible by experimenters with ssh or XDMCP.
CMC - It is the control and monitoring manager for all CM elements of ORBIT nodes. It is connected with CM port of nodes and can NOT share Ethernet port with Services and Console.
In our situation, Service and Console share one ethernet port with address 10.10.0.10/16 and CMC is on another ethernet port with address 10.1.200.1/16.
You may connect 10.10.0.10 and 10.1.200.1 with an internal route. In my situation. Since both machines connect to outside with their eth1, I explicitly set route on both machine as following.
On Console/Services
console:~# route add -host 10.1.200.1 gw 128.238.34.248 dev eth1 console:~# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface cmc.grid.poly.e cmc.local 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 eth1 localnet * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 10.10.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 default 128.238.34.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
On CMC
cmc:~# route add -host 10.10.0.10 gw 128.238.34.247 dev eth1 cmc:~# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface console.grid.po console.local 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 eth1 128.238.34.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1 10.1.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 default 128.238.34.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1 cmc:~# ping console PING console.grid.poly.edu (10.10.0.10) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from console.grid.poly.edu (10.10.0.10): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.128 ms 64 bytes from services.grid.poly.edu (10.10.0.10): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.139 ms
Software and Services
Linux Installation
You need install Linux on two or more machines. If you want to use only one machine, it must equipped with two or more ethernet interfaces. You can choose whatever Linux distribution you prefer. However, Debian is strongly recommended because some testbed related software are distributed in both source code and Deb package. The installation guide can be found here. For more information about Debian, please visit http://www.debian.org
Configure Apt
If the Linux distribution you choosed is Debian/Ubuntu, please add the following lines in file /etc/apt/sources.list, so let apt-get can find Debian packages provided by Orbit lab.
deb http://apt.orbit-lab.org/orbit testing main deb http://apt.orbit-lab.org/orbit unstable main deb http://apt.orbit-lab.org/orbit stable main
After each time sources.list is changed, please run command "apt-get update" to resynchronize the package index files from their sources. For more about sources.list and apt-get, please refer with command "man sources.list" and "man apt-get".
Configure host name
If Console/Service and CMC are on different machines, please edit file /etc/hostname respectively. The host name of Console/Service is "console", and that of CMC is "cmc". If the whole three server are on one machine, please set it's host name to "console".
Configure network interface
Since we place Console/Service and CMC on different machine. Interface configuration file should like following
For Console/Service
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system # and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5). # The loopback network interface auto lo eth0 eth1 iface lo inet loopback # The primary network interface access to outside internet allow-hotplug eth1 iface eth1 inet static address 128.238.34.247 netmask 255.255.255.0 network 128.238.34.0 broadcast 128.238.34.255 gateway 128.238.34.1 #iface eth1 inet dhcp ## dns-* options are implemented by the resolvconf package, if installed dns-nameservers 10.10.0.10 128.238.1.68 dns-search grid.poly.edu dns-domain grid.poly.edu # The internal network interface for console and services(nodehandler4, # dhcp, dns, gridservice2, OML, etc) allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 10.10.0.10 netmask 255.255.0.0 network 10.10.0.0 broadcast 10.10.255.255 ## dns-* options are implemented by the resolvconf package, if installed dns-nameservers 10.10.0.10 128.238.1.68 dns-search grid.poly.edu dns-domain grid.poly.edu
For CMC
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system # and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5). # The loopback network interface auto lo eth0 eth1 iface lo inet loopback # The primary network interface access to outside internet allow-hotplug eth1 iface eth1 inet static address 128.238.34.248 netmask 255.255.255.0 network 128.238.34.0 broadcast 128.238.34.255 gateway 128.238.34.1 # dns-* options are implemented by the resolvconf package, if installed dns-nameservers 10.10.0.10 128.238.1.68 dns-search grid.poly.edu dns-domain grid.poly.edu #iface eth1 inet dhcp # The internal network interface for CMC(gridservice). allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 10.1.200.1 netmask 255.255.0.0 network 10.1.0.0 broadcast 10.1.255.255 ## dns-* options are implemented by the resolvconf package, if installed dns-nameservers 10.10.0.10 128.238.1.68 dns-search grid.poly.edu dns-domain grid.poly.edu
In each server, interface eth0 is for test bed, and eth1 is for access outside. If all servers is on one machine, the configuration of eth0 on CMC should be moved to /etc/network/interfaces on Console/Services.
Name resolve
Because eth1 might connect with other DHCP/DNS servers from outside, and it used to change file /etc/resolv.conf when servers boot up, we need resolvconf to fix the setting in in resolv.conf.
First, install "resolvconf" with command "apt-get install resolvconf". Then, run command "dpkg-reconfigure resolvconf" and agree to symlink /etc/resolv.conf to /etc/resolvconf/run/resolv.conf. At last, edit file /etc/resolvconf/interface-order like following
# interface-order(5) eth*
Some comment for file /etc/network/interfaces:
"dns-nameservers 10.10.0.10 128.238.1.68" indicates resolvconf to add nameservers 10.10.0.10 and 128.238.1.68 in resolv.conf. 10.10.0.10 is the address of DNS used for testbed, and 128.238.1.68 is the address of DNS for outside, which you can change to others in your situation. Please make sure 10.10.0.10 is the first address appear in the list.
"dns-search grid.poly.edu" and "dns-domain grid.poly.edu" indicate resolvconf to add "search" and "domain" entries in resolv.conf. "grid" is considered as the name of test bed, which will be used in later configuration.
The final /etc/resolv.conf might looks like below after rebooting the machine.
# Dynamic resolv.conf(5) file for glibc resolver(3) generated by resolvconf(8) # DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE BY HAND -- YOUR CHANGES WILL BE OVERWRITTEN nameserver 10.10.0.10 nameserver 128.238.1.68 search grid.poly.edu
For more information about resolvconf, please refer /usr/share/doc/resolvconf/README.gz and "man resolvconf".
DHCP
Purpose: This software runs a DHCP server that assigns IP addresses to clients on demand.
Installation and Configuration: :
- Run command on Console/Services, and select eth0 as interface.
apt-get install dhcp3-server
- Make sure that /etc/default/dhcp3-server has eth0 as default interface which DHCP will server for. Just like following
# On what interfaces should the DHCP server (dhcpd) serve DHCP requests? # Separate multiple interfaces with spaces, e.g. "eth0 eth1". INTERFACES="eth0"
- Edit /etc/dhcp3/dhcpd.conf. The configuration looks like below.
# The ddns-updates-style parameter controls whether or not the server will # attempt to do a DNS update when a lease is confirmed. We default to the # behavior of the version 2 packages ('none', since DHCP v2 didn't # have support for DDNS.) ddns-update-style interim; use-host-decl-names on; allow booting; allow bootp; # option definitions common to all supported networks... option domain-name "grid.poly.edu"; default-lease-time 259200; max-lease-time 259200; # If this DHCP server is the official DHCP server for the local # network, the authoritative directive should be uncommented. #authoritative; # Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also # have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection). log-facility local7; subnet 10.10.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 { range 10.10.1.1 10.10.255.254; option domain-name "grid.poly.edu"; ddns-updates off; ddns-domainname "grid.poly.edu"; ddns-rev-domainname "in-addr.arpa"; option domain-name-servers 10.10.0.10; next-server 10.10.0.10; host services {hardware ethernet 00:1B:2F:BE:EF:94; fixed-address services.grid.poly.edu;} host console {hardware ethernet 00:1B:2F:BE:DF:6E; fixed-address console.grid.poly.edu;} filename "/tftpboot/pxelinux.bin"; #node 10.10.x.y group { host node1-1 {hardware ethernet 00:0F:EA:8C:AE:39; fixed-address node1-1.grid.poly.edu;} host node1-2 {hardware ethernet 00:03:2D:08:19:fe; fixed-address node1-2.grid.poly.edu;} host node1-3 {hardware ethernet 00:03:2D:07:67:CE; fixed-address node1-3.grid.poly.edu;} } }Some comments on the dhcpd.conf
First line is use-host-decl-names on which means DNS has actual IP mappings, DHCP just gives out hostnames. This means only IP to name updates need to be done only at DNS.
next-server is used to specify the host address of the server from which the initial boot file is to be loaded. In our case, it's the address tftp server.
The filename statement is used to specify the name of the initial boot file which is to be loaded by a client.
domain-name-servers specifies a list of Domain Name System name servers available to the client.
The node name in form of nodex-y determines it's address must be 10.10.x.y. For example, the address of node2-3 is 10.10.2.3. The actual address mapping is done by DNS.
To Run: : /etc/init.d/dhcp3-server start — errors go to /var/log/daemon.log
DNS
Purpose: Services.poly.edu” hosts the primary DNS service for the zone grid.poly.edu. The DNS server is the standard BIND9 software packaged.
Installation and Configuration: :
- apt-get install bind9
- You need edit Named.conf, named.conf.options and named.conf.local under /etc/bind as below
- named.conf
include "/etc/bind/named.conf.options"; include "/etc/bind/named.conf.local"; Controls { inet 127.0.0.1 port 953 allow { 127.0.0.1; }; }; // prime the server with knowledge of the root servers zone "." { type hint; file "/etc/bind/db.root"; }; // be authoritative for the localhost forward and reverse zones, and for // broadcast zones as per RFC 1912 zone "localhost" { type master; file "/etc/bind/db.local"; }; zone "127.in-addr.arpa" { type master; file "/etc/bind/db.127"; }; zone "0.in-addr.arpa" { type master; file "/etc/bind/db.0"; }; zone "255.in-addr.arpa" { type master; file "/etc/bind/db.255"; }; - named.conf.options
options { directory "/etc/bind"; auth-nxdomain no; # conform to RFC1035 listen-on-v6 { any; }; }; - named.conf.local
// Consider adding the 1918 zones here, if they are not used in your // organization //include "/etc/bind/zones.rfc1918"; zone "grid.poly.edu" IN { type master; file "/etc/bind/orbit.zone"; }; zone "in-addr.arpa" IN { type master; file "/etc/bind/zone.orbit"; };
- named.conf
- You need create orbit.zone and zone.orbit under /etc/bind as below
- orbit.zone: Forward lookup
$TTL 3600 @ IN SOA services.grid.poly.edu. root.services.grid.poly.edu. ( 2008072501 ; serial 3600 ; refresh (1 hour) 600 ; retry (10 min) 10000 ; expire (2 hours) 3600 ); ; @ IN NS services.grid.poly.edu. $ORIGIN grid.poly.edu. $TTL 129600 windows IN A 10.10.1.8 rxwarp IN A 10.10.1.9 node1-1 IN A 10.10.1.1 node1-2 IN A 10.10.1.2 node1-3 IN A 10.10.1.3 console IN A 10.10.0.10 cmc IN A 10.1.200.1 services IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. dhcp IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. frisbee IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. pxe IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. oml IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. repository IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. repository1 IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. repository2 IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. ntp IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. loghost IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. idb1 IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. idb2 IN CNAME console.grid.poly.edu. - zone.orbit: Reverse lookup
$TTL 3600 @ IN SOA services.grid.poly.edu. root.services.grid.poly.edu. ( 2008021817 ; serial 28800 ; refresh (8hours) 900 ; retry (15 mins) 604800 ; expire (1 week) 86400 ; minimum (1 day) ); @ IN NS services.grid.poly.edu. $ORIGIN in-addr.arpa. $ORIGIN 10.in-addr.arpa. $ORIGIN 0.10.10.in-addr.arpa. $TTL 129600 10 IN PTR services.grid.poly.edu. 10 IN PTR console.grid.poly.edu. $ORIGIN 1.10.10.in-addr.arpa. 9 IN PTR rxwarp.grid.poly.edu. 8 IN PTR windows.grid.poly.edu. 1 IN PTR node1-1.grid.poly.edu. 2 IN PTR node1-2.grid.poly.edu. 3 IN PTR node1-3.grid.poly.edu. $ORIGIN 200.1.10.in-addr.arpa. 1 IN PTR cmc.grid.poly.edu.
- orbit.zone: Forward lookup
- Make sure there are dots at the end of the domains. The owner and group of orbit.zone and zone.orbit might be like following.
console:/etc/bind# ls -l orbit.zone zone.orbit -rw-r--r-- 1 root bind 1217 2008-08-07 17:00 orbit.zone -rw-r--r-- 1 root bind 928 2008-08-07 17:01 zone.orbit
To Run: :
/etc/init.d/bind9 start — errors go to /var/log/daemon.log
- You may run command "host" on Console/Services or CMC as below to verify if bind works well.
console:~# host cmc cmc.grid.poly.edu has address 10.1.200.1 console:~# host console console.grid.poly.edu has address 10.10.0.10 console:~# host services services.grid.poly.edu is an alias for console.grid.poly.edu. console:~# host node1-1 node1-1.grid.poly.edu has address 10.10.1.1 console:~# host pxe pxe.grid.poly.edu is an alias for console.grid.poly.edu. console.grid.poly.edu has address 10.10.0.10 console:~# host frisbee frisbee.grid.poly.edu is an alias for console.grid.poly.edu. console.grid.poly.edu has address 10.10.0.10
Apache Web Server
Purpose: Apache server is required for maintaining the ORBIT local repository for debian packages and also to view the results of the experiment
Installation:
- apt-get install apache2
Note that no additional configuration is needed for apache. Also, make sure that /var/www/cgi-bin points to /usr/lib/cgi-bin (or create a soft link if one does not exist using cd /var/www/; ln –s /usr/lib/cgi-bin cgi-bin).
To run:/etc/init.d/apache2 start — errors go to /var/log/daemon.log
We also need install libgd, which is used to view the results of the experiment. The command below can install it
apt-get install libgd-gd2-perl
NTP
Purpose:
All the machines synchronize their time using the time server as the reference.
Installation and Configuration:
- apt-get install ntp
- You may add ntp server "pool.ntp.org" into /etc/ntpd.conf if there is server setting in it.
To run:
- /etc/init.d/ntpd start — errors go to /var/log/daemon.log
TFTP Server
Purpose: TFTP is needed to install PXE images whenever you need to install an image onto the node (using Frisbee). It is also used to load a memory based image that can be used to fetch the current image of the node into the repository
Installation and Configuration:
- apt-get install atftpd
There are two options here: either to run atftpd as a standalone daemon or run it under inetd. For heavy duty tftp services, you can choose to run is as a standalone daemon. For our installation, we choose the standalone daemon.
- Edit file /etc/inetd.conf and point the tftp directory to /tftpboot. The configuration may look like following
#:BOOT: TFTP service is provided primarily for booting. Most sites # run this only on machines acting as "boot servers." tftp dgram udp wait root /usr/sbin/atftpd /usr/sbin/in.tftpd /tftpboot
- The PXE image can be download from here. You need to extract it with command
tar -xjvf tftpboot.tar.bz2
The final content of directory /tftpboot looks like as below.
console:~# ls /tftpboot -R /tftpboot: initramfs-orbit-pxe-2.0.3.gz linux-orbit-pxe-2.6.25.1 pxelinux.bin pxelinux.cfg /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg: default orbit-2.0.3-omf
In case of problems, make sure that lo interface is up.
NFS Service
Purpose: This service is used to remotely mount directories on the nodes while fetching their image using imagezip utility. Also, Frisbee service makes use of this directory to install images onto nodes.
Installation and Configuration:
- apt-get install nfs-kernel-server
- create a path like "/export/orbit/image/tmp"
- Add a line in /etc/exports file as follows. "/export/orbit/image/tmp" is the default path nodes use to save frisbee images.
/export/orbit/image/tmp 10.10.0.0/16(rw,sync,no_root_squash)
To run:
- /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server start — errors go to /var/log/daemon.log
Mysql Server
Purpose: This service is used to store the results of the experiments conducted on ORBIT
Installation and Configuration:
- apt-get install mysql-server-4.1
- Edit /etc/mysql/my.cnf and replace bind-address from 127.0.0.1 to 10.10.0.10
type mysql and at the prompt, enter the following
- Replace the password by an appropriate one. Basically, this creates a new account called orbit with the password specified and allows access to mysql databases from localhost and any other machine on the network.
To run:
- /etc/init.d/mysql start — errors go to /var/log/mysql.log
ORBIT Server
Orbit specific services include nodehandler, nodeagent, frisbee, gridservices, gridservices2 and OML(Orbit Measurement Library). If you have added configuration in sources.list as described here, you can follow the commands below to install them. All these services are installed on Console, except gridservices on CMC.
For Console
- apt-get update
- apt-get install otg
- apt-get install nodehandler4
Since some files in nodehandler4 debian package are obsolete, you need to update it with a tar ball. Extract it and replace fold /opt/nodehandler4-4.2.0/.
The configuration of nodehandler4 is based on YAML script file /etc/nodehandler4/nodehandler.yaml. You can create a symbol link named "nodehandler.yaml" to the actual configuration file. The example and comments below could be helpful to understand it.1 # NOTE: use only 'spaces' to indent ! 2 # ('tab' indents are not supported by the ruby yaml parser used to read this file) 3 # 4 # This is the Config file for the NodeHandler4 on the WINLAB platform 5 # 6 --- 7 nodehandler: 8 name_resolv: | 9 name = nil 10 if NodeHandler.JUST_PRINT 11 name = 'debug' 12 else 13 # take first subdomain as grid name (sb0.orbit-lab.org) 14 IO.popen('hostname -d') {|f| name = f.gets.split('.')[0] } 15 end 16 17 testbed: 18 19 # Config Parameter for the "default" Testbed 20 # 21 # In the WINLAB setting the default testbed is the "grid" testbed, using gridservice2 22 default: 23 24 repository: 25 path: [".", "../repository", "/opt/nodehandler4-4.2.0/repository"] 26 27 pxe: 28 # This is the URL where NH can find the PXE GridService 29 url: 'http://pxe:5022/pxe' 30 31 cmc: 32 # This is the URL where NH can find the CMC GridService 33 url: "http://cmc:5012/cmc" # Contact the CMC of GS 1 - Not ported yet for GS 2 34 35 oml: 36 # NodeAgents will use the numerical IP address in 'local_host' to connect 37 # to the machine running the NodeHandler, in order to retrieve the OML defs 38 # (in XML, and generated by NH). These OML defs are used by the NAs' applications 39 # Thus, 'local_host' = Control IP address (reachable by NAs) of the NH's machine 40 local_host: '10.10.0.10' 41 # The parameters below are the contact details for the OML GridService 42 url: "http://oml:5022/oml" 43 port: 5022 44 host: "oml" 45 46 frisbee: 47 # The parameters below are the contact details for the Frisbee GridService 48 default_disk: '/dev/sda' 49 url: 'http://frisbee:5022/frisbee' 50 51 inventory: 52 # This is the URL where NH can find the inventory GridService 53 url: 'http://cmc:5022/inventory' 54 55 # Command used to launch the communication module 56 # The type of comm module to launch depends on the cmd line params 57 # '-c PORT' runs a TCP comm. module that will connect to the node Agent's TCP server on PORT 58 # '-l PORT' runs a TCP comm. Server module that will listen for node Agent's connection on PORT 59 # default: runs a Multicast comm. module 60 # 61 # The following line runs the commServer in TCP Client Mode 62 #commServer: /opt/nodehandler4-4.2.0/sbin/commServer --logfile /tmp/commServer-%ID%.log -d 4 --iface eth1 -c 9026 63 # The following line runs the commServer in Multicast Mode 64 commServer: /opt/nodehandler4-4.2.0/sbin/commServer --logfile /tmp/commServer-%ID%.log -d 4 --iface eth0 65 66 # 67 # Return the IP address of the control interface of 68 # the node a coordinates x:y 69 # 70 # @param x X coordinate of node 71 # @param y Y coordinate of node 72 # 73 controlIp: | 74 |x, y| 75 # This is the Node Agents control IP address used in the WINLAB grid testbed 76 "10.10.#{x}.#{y}" 77 78 # 79 # Return the x:y coordinates of a node signing on with 80 # 'idString'. This string is supposed to be of the type 81 # '/ip/CONTROL_IP'. 82 # 83 # @param idString String of type '/ip/CONTROL_IP' 84 # @return Array of [x, y] 85 # 86 nodeId2coord: | 87 |idString| 88 match = /.*\.(\d+)\.(\d+)$/.match(idString) 89 if (match != nil && match.size == 3) 90 x = match[1].to_i 91 y = match[2].to_i 92 if x > 100 93 # sandbox 94 x = y / 100 95 y = y % 100 96 end 97 return [x, y] 98 end 99 raise "Can't parse #{idString}" 100 101 # Return the control IP address (as string) or DNS name for a node 102 # at a given coordinate. 103 # 104 # Throws an ConfigException if no IP address can be found. 105 # In this testbed, nodes are identified using only 1-dimensional coordinate: X 106 # (At WinLab, nodes are identified using 2D coordinates) 107 # 108 coord2ip: | 109 |x, y| 110 # This is the base name used in the WINLAB testbeds 111 name = "node#{x}-#{y}" 112 begin 113 Socket.gethostbyname(name)[3].unpack('C4').join('.') 114 rescue SocketError 115 raise("Unknown host '#{name}'") 116 end 117 118 load: | 119 | uri, evalRuby | 120 path = [ uri.split(':').join('_') + '.rb'] 121 postfix = '/' + uri.split(':').join('/') + '.rb' 122 REPOSITORY_DEFAULT().each { |dir| 123 path << dir + postfix 124 } 125 #puts "PATH: #{path.join(':')}" 126 file = path.inject(nil) { |found, p| 127 if found == nil && File.readable?(p) 128 found = p 129 end 130 found 131 } 132 if file == nil 133 raise IOError, "Can't find any of '#{path.join(', ')}'" 134 end 135 str = File.new(file).read() 136 if evalRuby 137 #eval(str, nil, path, 1) 138 require file 139 end 140 [str, 'text/ruby'] 141 142 # Config Parameter for the "grid" Testbed 143 # 144 # To use this testbed, call nodeHandler with the option "-d grid" 145 # Any parameter settings within this section will override the settings 146 # done in the "default" section. The nodeHandler fisrt load the "default" 147 # settings, then it uses the "domain" specific settings to override the 148 # relevant parameters 149 # 150 # For more details: see comments in "default" domain section 151 grid: 152 X_MAX: 2 153 Y_MAX: 20 154 oml: 155 local_host: '10.10.0.10' 156 url: "http://oml:5022/oml" 157 port: 5022 158 host: "oml" 159 controlIp: | 160 |x, y| 161 "10.10.#{x}.#{y}" 162 163 # Config Parameter for the "debug" Testbed 164 # 165 # To use this testbed, call nodeHandler with the option PRINT_ONLY or "-d debug" 166 # Any parameter settings within this section will override the settings 167 # done in the "default" section. The nodeHandler fisrt load the "default" 168 # settings, then it uses the "domain" specific settings to override the 169 # relevant parameters 170 debug: 171 repository: 172 path: ['../repository'] 173 commServer: ../c/commServer/commServer -d 4 --iface eth0 174 coord2ip: | 175 |x, y| 176 "10.99.#{x}.#{y}"
Comments:
Line 29: PXE is one of services from gridservices2, and 5022 is its default port. Please make sure http://pxe could be resolved from Console.
Line 33: CMC is the only service provided by gridservices, and 5012 is its default port. In my situation. The address is http://cmc is 10.1.200.1.
Line 48: '/dev/sda' is the paramter frisbee need to image hard drivers. If the hard drivers in nodes are equipped with ATA interface, Please change it to "/dev/hda"
Line 49: Similar with PXE, it's also a service by gridsercies2.
Line 64: This is command used to launch the communication module of Nodehandler4. The value for parameter "—iface" should be the interface with IP address 10.10.0.10.
Line 151: "grid" is the name of testbed which must match with the first word of domain name of Console. For example, the output of command "hostname -d" is "grid.poly.edu", so "grid" is the name of testbed.
Line 152,153: The maximum value of two dimensions of testbed. If the Control port of each node has IP address 10.10.x.y, the node's hostname should be like nodex-y.grid.poly.edu, which is controlled by DNS. x and y are intergers less than X_MAX and Y_MAX respectively.
- frisbee package is an dependency of gridservices2, which can be downloaded from here and install it with command
dpkg -i frisbee_1.0.3-1_i386.deb
You can also get the latest source code of frisbee from here if you prefer to build it in your own system. You need get at least 2 executable files, frisbeed and frisbee. If you want make frisbee images, you must build imagezip from source code, which is not provided by frisbee debian package. For more information about frisbee, please vist http://www.emulab.net/software.php3 or read "README" attached with the source code.
- apt-get install gridservices2 oml-collection-server
The configuration of gridservices2 is under path /etc/gridservices2, Please go through README.txt under it first. Gridservices2 must enable at least 2 services, frisbee and PXE. The configuration of frisbee, frisbee.yaml, looks like below1 # NOTE: use only 'spaces' to indent ! 2 # ('tab' indents are not supported by the ruby yaml parser used to read this file) 3 # 4 # This is the Config file for the Frisbee GridService on the NICTA platform 5 # 6 --- 7 frisbee: 8 9 # Max. number of active daemons allowed 10 maxDaemons: 10 11 12 testbed: 13 default: 14 # Directory images are stored 15 imageDir: /home/node 16 defaultImage: baseline0.4 17 18 # max bandwidth for frisbee server 19 bandwidth: 50000000 20 21 # Multicast address to use for servicing images 22 mcAddress: 224.0.0.2 23 # Using ports starting at ... 24 startPort: 7000 25 26 # Time out frisbee server if nobody requested it within TIMEOUT sec 27 timeout: 3600 28 29 # Directory to find frisbee daemon 30 frisbeeBin: /usr/sbin/frisbeed 31 32 # Local interface to bind to for frisbee traffic 33 multicastIF: 10.10.0.10 34 35 indoor: 36 imageDir: /home/node 37 defaultImage: baseline0.4 38 bandwidth: 50000000 39 mcAddress: 224.0.0.2 40 startPort: 7000 41 timeout: 3600 42 frisbeeBin: /usr/sbin/frisbeed 43 multicastIF: 10.10.0.10
Comments:
Line 15: The place where frisbee image files are places.
Line 16: The file name of image without "ndz" suffix. For example, if file name is baseline0.4.ndz, it should be set to baseline0.4. The file will be the default image when no explicit image is given in omf command.
Line 19: The maximum bandwidth in bps which frisbee can use to image hard drivers.
Line 30: The place where gridservices2 can find frisbeed.
The configuration of PXE, pxe.yaml, looks like below.
1 pxe:
2 # Name of PXE config file
3 defImage: orbit-2.0.3-omf
4
5 # Directory pxe config files are stored
6 cfgDir: /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
7
8 # Maximum age of PXE symbolic link [sec]
9 linkLifetime: 900
10 # linkLifetime: 5 # for testing only
11
12 # toIP: mapping from x@y to IP address
13 # listAll: return array of x/y coodinates of all nodes in '[x,y]' form.
14 #
15 testbed:
16 default:
17 toIP: |
18 |x,y|
19 assertRange(x, 1..1, "unknown node #{x}@#{y}")
20 assertRange(y, 1..20, "unknown node #{x}@#{y}")
21 "10.10.#{x}.#{y}"
22 listAll: |
23 defGrid(1,4)
If all configuration are done, run following command to start gridservices2
- /etc/init.d/gridservices2 start
For CMC,
- apt-get install libmysqlclient15
- apt-get install gridservices
Some files of gridservices needs upgrade. Get a tar ball and extract it to replace fold /ect/gridservices.
Gridservices ONLY provides CMC service. It's configuration is defined in file /ect/gridservices/cmc.yaml, which looks like below.
1 primaryIF: "128.238.34"
2 communicators:
3 default: &comm_default
4 ip: 10.1.200.1
5 port: 9030
6
7 testbeds:
8 grid:
9 x_max: 2
10 y_max: 20
11 ip_block: lambda {|x,y| "10.1.#{x}.#{y}"}
12 inactive_list: [ ]
13 3vStatus: 0.016
14 5vStatus: 0.032
15 12vStatus: 0.064
Comments:
Line 1: This line defines the network address of the interface which connects to outside network. In my situation, CMC and Console are connected within network 128.238.34.*.
Line 4: This line define the IP address of the interface which connects to the nodes.
Line 9,10: The maximum value of two dimensions of testbed. The CM port of each node has IP address 10.1.x.y, which is within the same network with 10.1.200.1.
If all configuration are done, run following command to start gridservices
- /etc/init.d/gridservices start
If gridservices starts successfully, you can input the address below in web browser. You will find a couple of commands provided by CMC on web page and you can control CMC with the web interface.
About the CM
The ORBIT Chassis Manager (CM) is a simple, reliable, platform-independent subsystem for managing and autonomously monitoring the status of each node in the Witestbed. Basically, it is a small PCI card port on the node. Administrators can turn on/off and reboot nodes remotely and monitor the status of nodes throught CM. User can access CM through serial console or telnet. For example. If a node's name is node2-3. the IP address of its control port is 10.10.2.3 and that of its CM port is 10.1.2.3. We can telnet to CM with command,
- telnet 10.1.2.3
We can also telnet to the node with either of two commands below
- telnet 10.1.2.3 3025
- telnet 10.10.2.3
If you want to access CM through serial console, please set the baud rate to 57600kps.
Updating the node BIOS
The new BIOS fixes some bugs and provides better support to network boot and power management. The detail description could be found here.
Attachments (3)
- node-50.png (41.3 KB ) - added by 17 years ago.
- orbit_node.JPG (40.1 KB ) - added by 17 years ago.
- testbed.PNG (33.1 KB ) - added by 17 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip
