Programmable Metamaterial Antenna For Physical Layer Security
Members: Dylan Turner [UG], Prachi Patel [UG]
Project Advisors and Mentors: Narayan Mandayam, Chung-Tse Michael Wu, Hariharan Venkat
PROJECT OVERVIEW
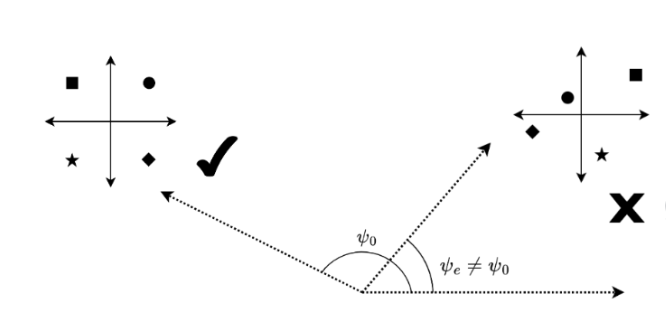
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution, there is an increasing need to develop low-cost physical layer security protocols for devices. These security protocols are essential for safeguarding the vast and diverse network of interconnected devices that form the IoT ecosystem. This will reduce the computational power that is required and propagate energy savings to potentially tens of billions of IoT devices. This project proposes a computationally simpler solution that uses Metamaterial antenna arrays that scramble the signal for eavesdroppers from undesired directions. This is called Directional Modulation.
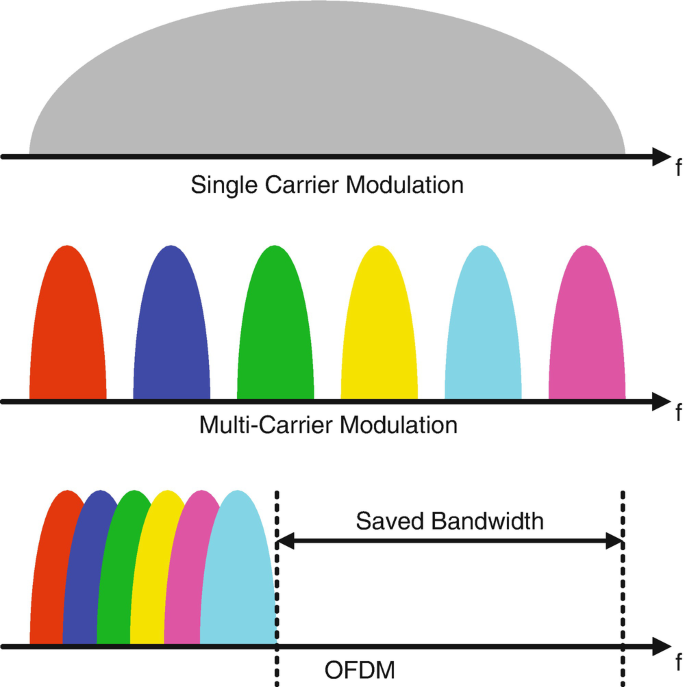
Previous researchers who have worked on this idea have successfully used Directional Modulation to securely transmit small amounts of data using low bandwidth. A problem arises however when larger amounts of data are transmitted, which require more bandwidth. It turns out that the Metamaterial Antenna is frequency-dependent. This means data sent on subcarrier waves with large differences in frequency ranges will be affected differently by the antenna, resulting in errors.
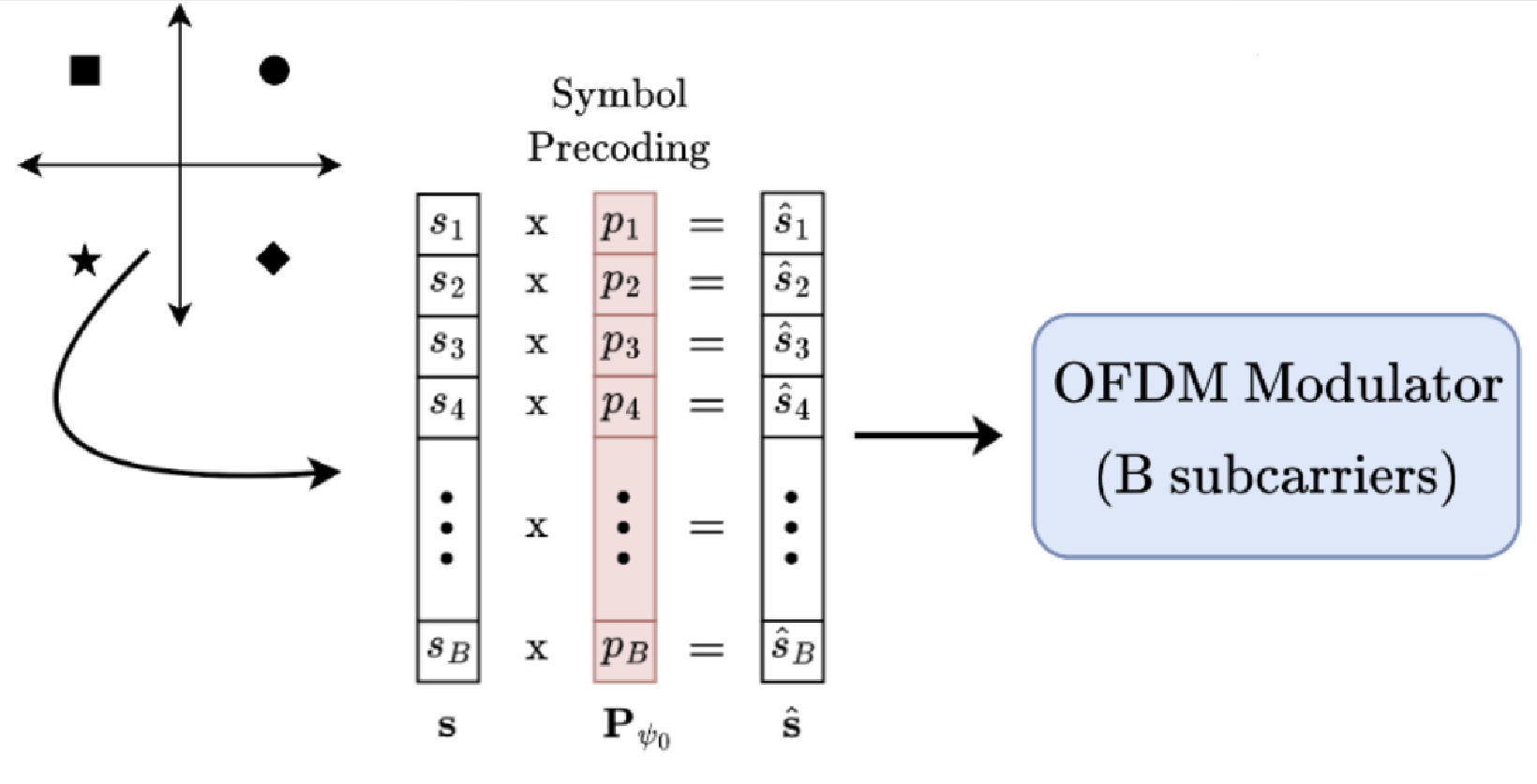
The solution to this problem, and the focus of our research this summer, is called Symbol Precoding.
Technologies: GNU Radio
PROGRESS LOG
Week 1 (5/28/24 - 5/30/24)
- The first week was spent meeting with our mentor Hariharan Venkat who presented us with a high-level overview of the project.
- Spent much of the day reading the research paper and proposal the project is based on, learning fundamental details of the research.
- Learned how to interface with the ORBIT and COSMOS test bed, and practiced connecting and sending commands to nodes.
Week 2 (6/3/24 - 6/6/24)
- Familiarized with fundamentals of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM).
- Attended the Introduction to Linux presentation.
- Installed and configured GNU Radio on our local devices.
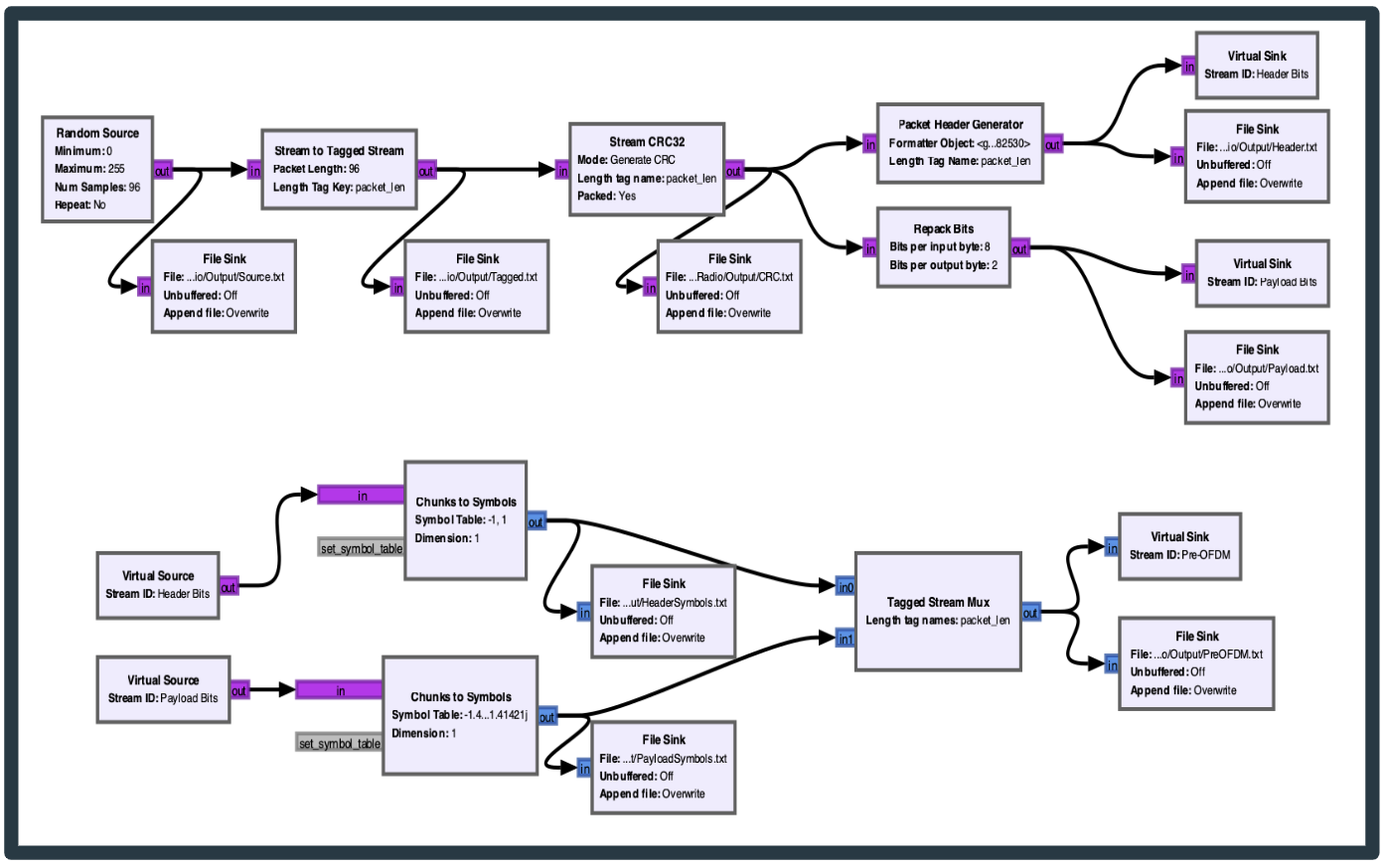
- Investigated how flowgraphs are converted into Python code, as well as the source code of the built-in OFDM_TX block.
- Experimented with creating flow graphs in GNU Radio.
- Completed a tutorial with our mentor using COSMOS Sandbox 2, transmitting and receiving OFDM signals from two Software Defined Radios (SDR).
Week 3 (6/10/24 - 6/13/24)
- Learned how to output to file sink in GNU Radio, allowing us to investigate precisely how data is manipulated through the flow graph.
- Traced through the flow graph for the OFDM_TX, viewing the binary output of each block and figuring out its purpose.
- Studied the implementation and purpose of the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) block.
- Wrote a Python script to convert the complex numbers in Single precision IEEE 752 format to decimal for better human readability.
- Attempted to find a way to visualize the output of the OFDM Carrier allocator, but ran into issues because we cannot open Embedded Python blocks on Mac OS due to a GNU Radio bug. Resulted to using a Windows Emulator as a workaround.
- Created a Custom Python Block which multiplies the first input vectors by the second input vectors. This is an important step for Symbol Precoding, where we multiply the transmitted symbol vector by a precoding vector.
Week 4 (6/17/24 - 6/20/24)
- Created custom python blocks to interact with OFDM Carrier Allocator Block:
- Prints its output in a readable format.
- Multiplies *specified* carriers by precoded vector.
- Studied the math that goes into Symbol Precoding vector calculation.
- Began implementing these functions using Python so we can complete our system and begin testing.
- After finishing the Precoding Calculation functionality we brought it into GNU Radio as a custom block and fixed many bugs.
Week 5 (6/24/24 - 6/27/24)
- Spent many hours comparing output of Hari's matlab code with our new GNU Radio block's output to ensure correct precoding calculations.
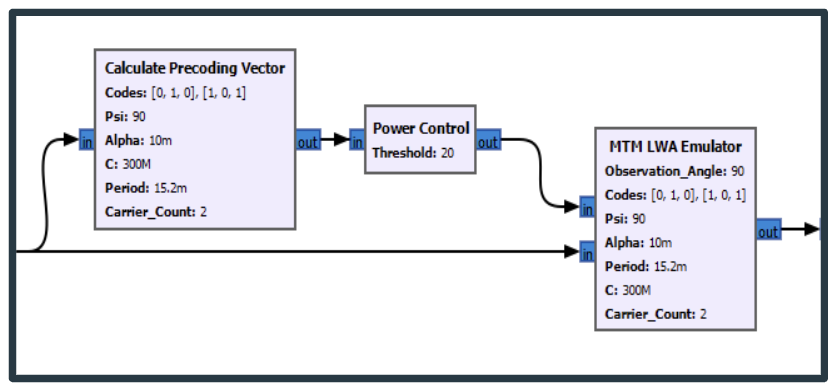
- Created an Emulator block for testing which would simulate the effects of the antenna on our signal digitally.
- Created a Power Control block to ensure that we do not supply a dangerous voltage to our Metamaterial Antenna when we begin real world experiments.
Week 6 (7/1/24 - 7/3/24)
- Modified our custom Python blocks to ensure consistent processing of chunks. This was an issue as a couple of the blocks were processing more data than needed at once, causing downstream blocks to halt unnecessarily.
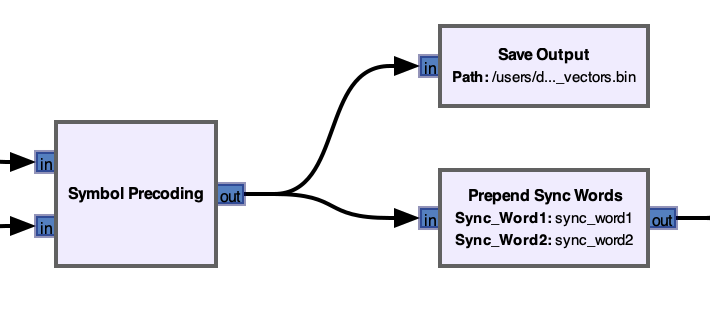
- Hari informed us that our method of utilizing sync words might have been misguided, and we reorganized our flowgraph to reflect these changes. This involved removing sync words from our precoding vector calculations and prepending them to the output.
- Researched the Sychmidl and Cox synchronization method.
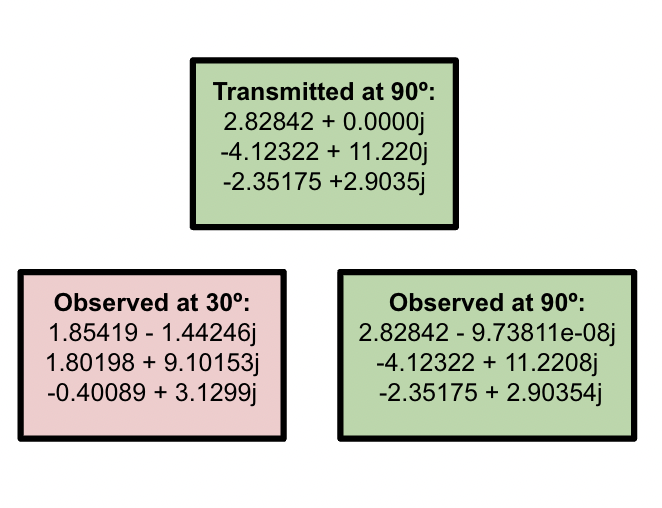
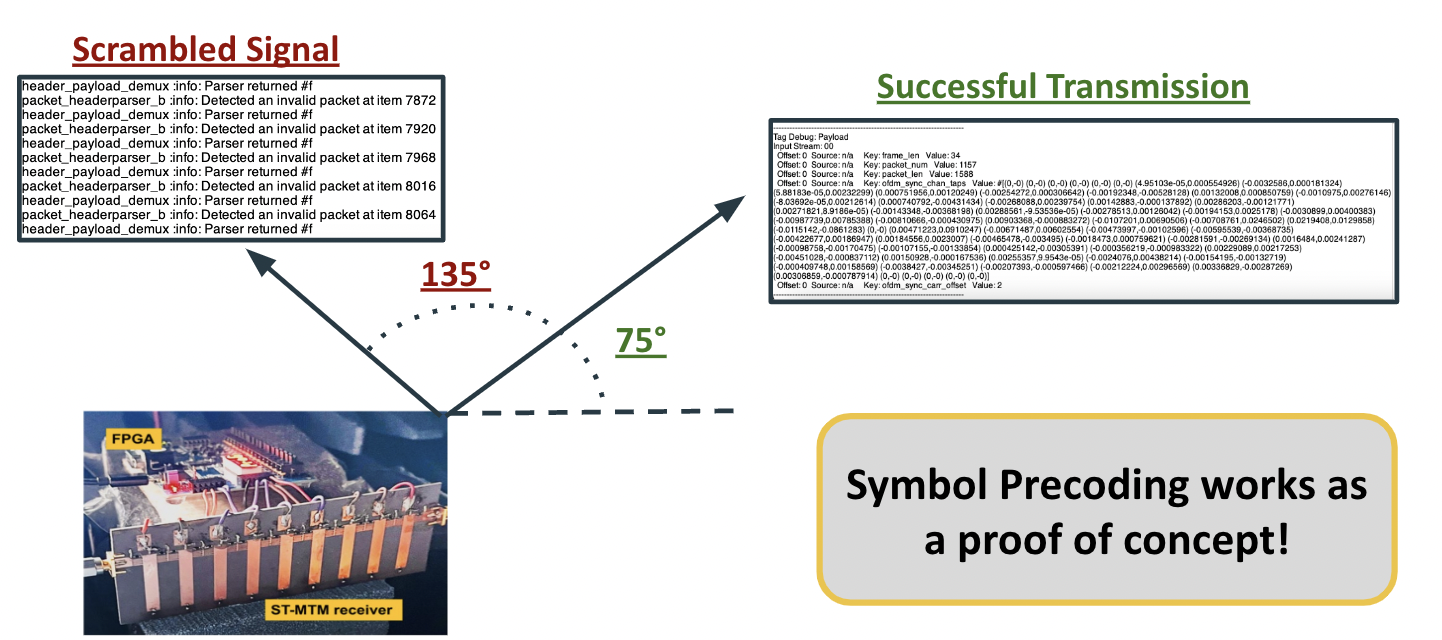
- Fixed small bugs in the Emulator Block, resulting in promising results! As the image below shows, observing a signal from an incorrect angle showed scrambled data, while the correct angle preserved it.
Week 7 (7/8/24 - 7/11/24)
- Found a solution that allowed us to create blocks with different length inputs and outputs. In this case, our Prepend Sync Words block needed to take in 9 payload vectors, concatenate 2 sync words and output those 11 vectors. (Surprisingly challenging)
- Major refactoring of our custom blocks to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Dynamically update matrix size depending on transmission content.
- Calculated a packet length to ensure fully utilized carriers in each transmission.
- Figured out a way to use GNURadio on MacOS, which is much quicker than using a Windows virtual machine.
Week 8 (7/15/24 - 7/18/24)
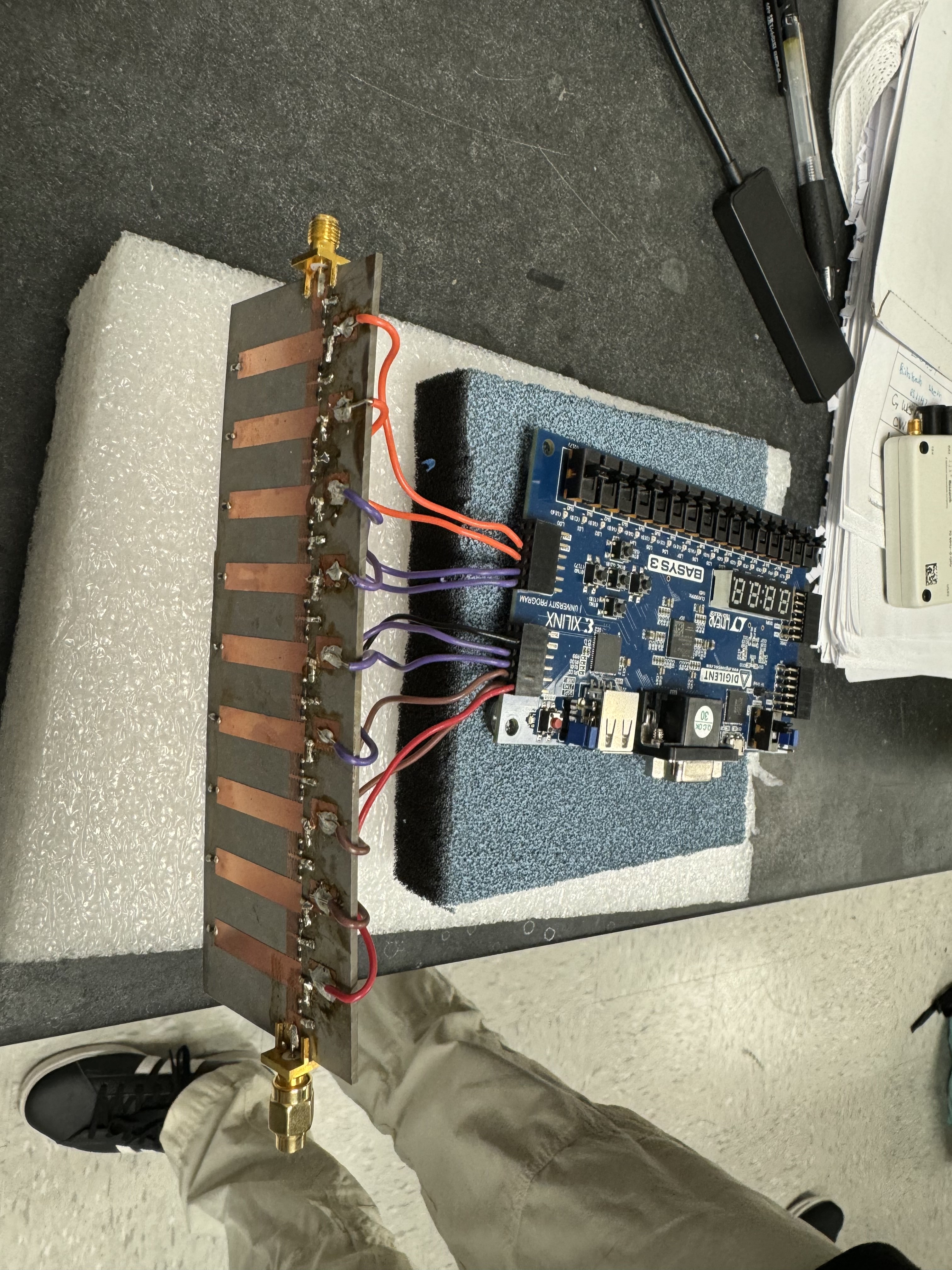
- Visited the Anechoic chamber in the Electrical Engineering building on Busch Campus.
- Prepared our antenna and FPGA in the anechoic chamber and became familiar with the room.
- Figured out a method that would allow us to precode our sync words, something we had previously not been able to do. Rather than exclude the sync words from our precoding, we simply replace the zeros in the sync words with random non-zero symbols, and then do the same calculations. In the end, we multiply by the original symbols anyway, which restores the original sync words.
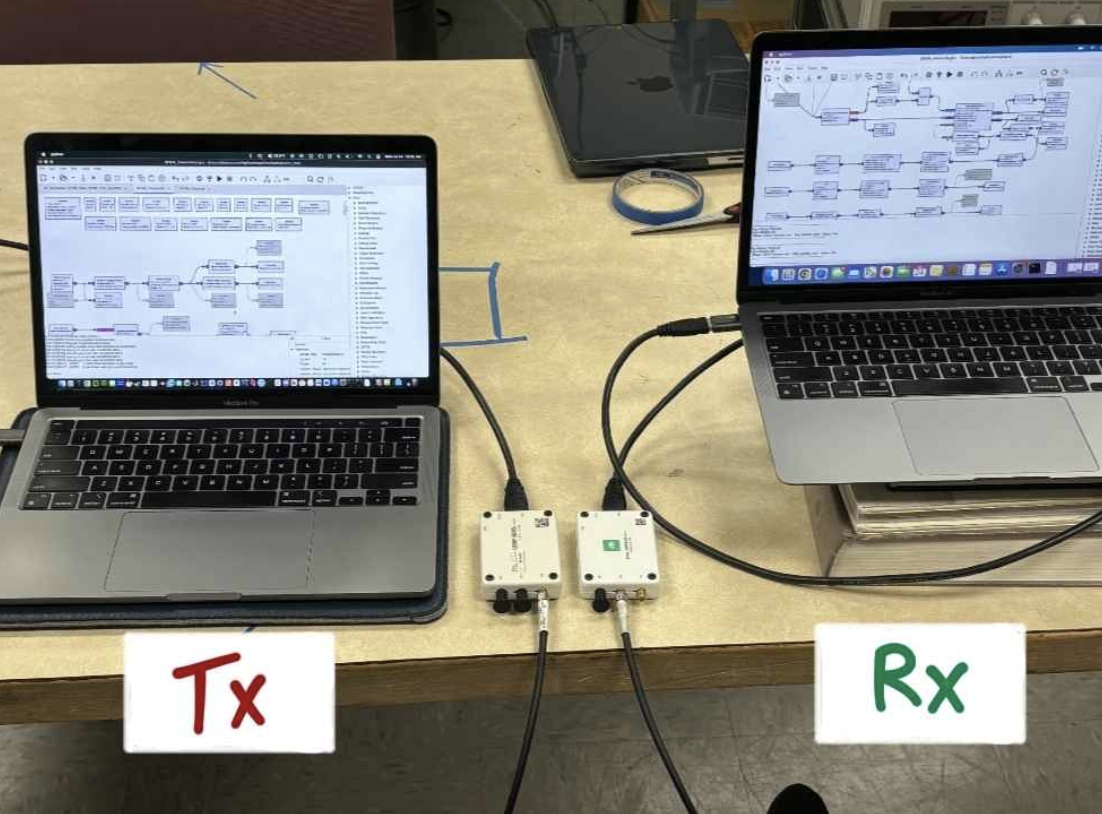
- Learned how to connect to the USRP’s, and transmit a signal over antenna and wire.
- Encountered many bizarre issues related to the USRP's in the lab. Experiments that had mostly worked previously on COSMOS Sandbox 2 were not working on the on-site USRP's.
Week 9 (7/22/24 - 7/25/24)
- Tested our system using the onsite USRPs with a wire and antenna connection.
- Padded each packet with zeros since our system dropped the last couple packets at the end.
- Lowered the sample rates because the tests worked on Sandbox 2, but not the onsite USRPs. Our FPGA was coded to only take in 20 MHz, and we did not have access to change the code.
- Ensured reception of all packets after implementing these changes.
Week 10 (7/29/24 - 8/1/24)
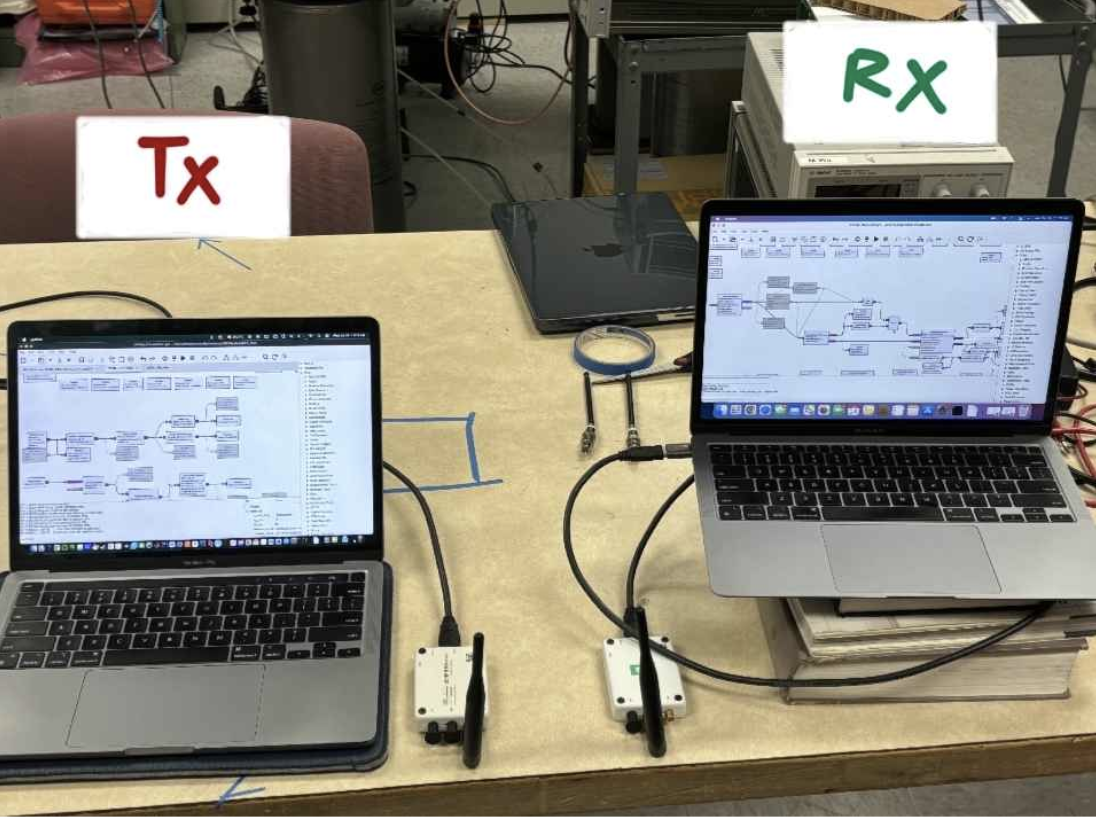
- Tested our system in the anechoic chamber on Busch.
- Split up our system into online and offline processing because it was too much processing to happen in real time.
- Received a small percentage of packets, but demonstrated proof of concept, confirming that symbol precoding works.
References
Nooraiepour, Alireza, et al. “Programming Wireless Security Through Learning‐Aided Spatiotemporal Digital Coding Metamaterial Antenna.”
Advanced Intelligent Systems, vol. 5, no. 10, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202300341.
Attachments (15)
- directional_modulation.png (32.0 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- symbol_precoding.png (162.3 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- OFDM_TX_flowgraph.png (286.4 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- precoding_math.png (115.5 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- custom_blocks.png (74.3 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- promising_results.png (83.8 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- promising_results.2.png (190.7 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- 1. Programming Wireless Security Through Learning‐Aided Spatiotemporal Digital Coding Metamaterial Antenna.pdf (17.5 MB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- prepend.png (36.8 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- Anechoic.png (931.3 KB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- MTMAntenna.jpg (4.8 MB ) - added by 20 months ago.
- Antenna.png (1.1 MB ) - added by 19 months ago.
- Wire.png (1.1 MB ) - added by 19 months ago.
- OFDM.png (85.1 KB ) - added by 19 months ago.
- Results.png (698.7 KB ) - added by 19 months ago.