| Version 1 (modified by , 3 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
Kubernetes Wiki Doc:
Table of Contents
Tutorial: Kubernetes Setup
Requirements:
- Setup/Practice of Orbit Nodes.
- Any available Orbit Sandbox Node
- Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS or Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS (Choice is up to you)
In this tutorial, we will be using one of the sb1 nodes for setting up Kubernetes. However, sb(1-10) should also be capable for Kubernetes setup.
Make sure you have Ubuntu 20.04.5 (baseline20.04.ndz) or 22.04.2 (ubuntu2204-beta.ndz) LTS. To get the Ubuntu Version, follow these steps after ssh'ing into your console. Substitute for the image and node you want.
The below steps illustrate loading Ubuntu 20.04.5 LTS for node1-2 of sb1. For the sb1 console,
username@console:~$ omf tell -t node1-2 -a offh
username@console:~$ omf load -t node1-2 -i baseline20.04.ndz
username@console:~$ omf tell -t node1-2 -a on
To verify if you have loaded your Ubuntu version properly, use this command after ssh into the node1-2
root@node1-2:~# lsb_release -a
This will list the current version of Ubuntu loaded.
Example Image:
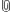
Set up a Kubernetes Cluster
After loading your version of Ubuntu, you can follow the below steps to install Kubernetes
- Update and Upgrade Packages:
root@node1-2:~# sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
- Install Docker:
root@node1-2:~# sudo apt install docker.io
- Configure Docker to use systemd for the management of the container’s cgroups:
root@node1-2:~# cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json { "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"], "log-driver": "json-file", "log-opts": { "max-size": "100m" }, "storage-driver": "overlay2" } EOF
- Enable Docker:
root@node1-2:~# sudo systemctl enable docker
- Reload the systemd manager configuration:
root@node1-2:~# sudo systemctl daemon-reload
- Restart Docker:
root@node1-2:~# sudo systemctl restart docker
- Update and Upgrade Packages again:
root@node1-2:~# apt update && apt upgrade -y
- Add Kubernetes to the repository list:
root@node1-2:~# curl -sSL https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
root@node1-2:~# echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
- Install Kubernetes:
root@node1-2:~# sudo apt-get update
root@node1-2:~# sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
root@node1-2:~# sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
- Initialize the Kubernetes Cluster:
root@node1-2:~# kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.19.0.0/16
You should see an output which includes a kubeadm join command, save this command for use on the worker nodes.
- Set KUBECONFIG environment variable:
root@node1-2:~# export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
- Apply Flannel network overlay:
root@node1-2:~# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
Joining Worker Nodes to the Cluster
To join worker nodes to the Kubernetes cluster, run the kubeadm join command that was outputted by the kubeadm init command.
Example:
root@node1-2:~# kubeadm join 10.19.1.5:6443 --token o1cttx.z9al8w8ljqcmqb4y --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:6ecd74d7eca0299b80499cf2e2e1c87c4079c3d234282be5822761880998853e
Hope You Figure Out the Purpose of Kubernetes
Attachments (1)
-
final node status.png
(63.8 KB
) - added by 3 years ago.
Node Status
Download all attachments as: .zip
